UK team promotes proper use of antibiotics to help thwart development of bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics
By the Antimicrobial Stewardship Team
UK HealthCare Pharmacy Services
In the U.S., more than 2.8 million antimicrobial-resistant infections occur each year. Antimicrobials — a group of essential medications including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals and antiparasitics — are used to prevent and treat infections in humans, animals and plants.
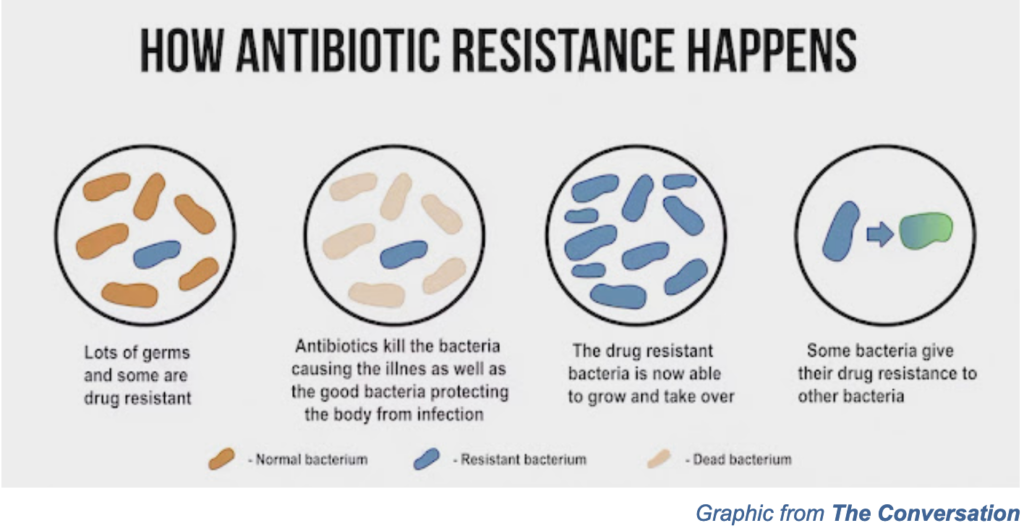
Antimicrobial resistance happens when germs like bacteria evolve to defeat the drugs that have been designed to kill them. Resistance has the potential to affect people at any stage of life, as well as health care, veterinary and agriculture industries. This makes antimicrobial resistance one of the world’s most urgent public health problems. Antibiotics can save lives when used appropriately to fight off bacterial infections, but they are not always the answer.
Here is some important information about responsible antibiotic use:
- Antibiotics do NOT treat viruses, like those that cause colds, flu, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or Covid-19. Other medications, like antivirals, can treat viruses.
- Antibiotics are only needed for treating certain infections caused by bacteria, but even some bacterial infections get better without antibiotics.
- When antibiotics aren’t needed they won’t help you and the side effects could still cause harm.
- If you need antibiotics, take them exactly as prescribed. Talk with your health care providers if you develop side effects or have questions about your antibiotics.
- Do your best to stay healthy and keep others healthy. This helps reduce antibiotic use and fights antimicrobial resistance.
What should you do when you feel sick?
- Contact your primary care provider.
- If you have been prescribed an antibiotic, take it the way it has been prescribed to you.
- Keep yourself and others around you healthy by washing your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or using hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol, covering your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze, staying home when you are feeling under the weather, and getting all recommended vaccines like the yearly flu vaccination.
For more information, follow the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s initiative, Be Antibiotics Aware: Smart Use, Best Care at www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/index.html.
About UK HealthCare’s antimicrobial stewardship
At UK HealthCare, a dedicated team of pharmacists and physicians are fighting the battle against drug-resistant infections every day. The antimicrobial stewardship team is committed to overseeing the type, dose and duration of antimicrobials our patients receive to ensure the best possible clinical outcomes.
The mission of UK HealthCare’s antimicrobial stewardship program is to optimize antimicrobial use to improve clinical outcomes and decrease the spread of resistance.
“The antimicrobial stewardship team is on clinical services, so we evaluate patients and provide guidance on the right dose and duration of antibiotics through the ID-consult service,” said Donna Burgess, pharmacy coordinator of the antimicrobial stewardship program. “If antibiotics are not needed, we are able to discontinue use in order to decrease antibiotic resistance and protect patients from potential side effects.”